15,446
社区成员
 发帖
发帖 与我相关
与我相关 我的任务
我的任务 分享
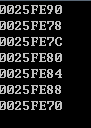
分享int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int a;
int b[3];
int c;
printf("%p\n",&a);
for(int i=-1;i<=3;i++)
printf("%p\n",&b[i]);
printf("%p\n",&c);
return 0;
}#include <stdio.h>
#define field_offset(s,f) (int)(&(((struct s *)(0))->f))
struct AD { int a; char b[13]; double c;};
#pragma pack(push)
#pragma pack(1)
struct A1 { int a; char b[13]; double c;};
#pragma pack(2)
struct A2 { int a; char b[13]; double c;};
#pragma pack(4)
struct A4 { int a; char b[13]; double c;};
#pragma pack(8)
struct A8 { int a; char b[13]; double c;};
#pragma pack(16)
struct A16 { int a; char b[13]; double c;};
#pragma pack(pop)
int main() {
printf("AD.a %d\n",field_offset(AD,a));
printf("AD.b %d\n",field_offset(AD,b));
printf("AD.c %d\n",field_offset(AD,c));
printf("AD sizeof %d\n", sizeof(AD));
printf("\n");
printf("A1.a %d\n",field_offset(A1,a));
printf("A1.b %d\n",field_offset(A1,b));
printf("A1.c %d\n",field_offset(A1,c));
printf("A1 sizeof %d\n", sizeof(A1));
printf("\n");
printf("A2.a %d\n",field_offset(A2,a));
printf("A2.b %d\n",field_offset(A2,b));
printf("A2.c %d\n",field_offset(A2,c));
printf("A2 sizeof %d\n", sizeof(A2));
printf("\n");
printf("A4.a %d\n",field_offset(A4,a));
printf("A4.b %d\n",field_offset(A4,b));
printf("A4.c %d\n",field_offset(A4,c));
printf("A4 sizeof %d\n", sizeof(A4));
printf("\n");
printf("A8.a %d\n",field_offset(A8,a));
printf("A8.b %d\n",field_offset(A8,b));
printf("A8.c %d\n",field_offset(A8,c));
printf("A8 sizeof %d\n", sizeof(A8));
printf("\n");
printf("A16.a %d\n",field_offset(A16,a));
printf("A16.b %d\n",field_offset(A16,b));
printf("A16.c %d\n",field_offset(A16,c));
printf("A16 sizeof %d\n", sizeof(A16));
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
//AD.a 0
//AD.b 4
//AD.c 24
//AD sizeof 32
//
//A1.a 0
//A1.b 4
//A1.c 17
//A1 sizeof 25
//
//A2.a 0
//A2.b 4
//A2.c 18
//A2 sizeof 26
//
//A4.a 0
//A4.b 4
//A4.c 20
//A4 sizeof 28
//
//A8.a 0
//A8.b 4
//A8.c 24
//A8 sizeof 32
//
//A16.a 0
//A16.b 4
//A16.c 24
//A16 sizeof 32
//
//