80,481
社区成员
 发帖
发帖 与我相关
与我相关 我的任务
我的任务 分享
分享public class MainActivity extends Activity {
TextView tv1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv1 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv1);
String s = "<g color='blue'>自定义</g>";
tv1.setText(Html.fromHtml(s, null, new GameTagHandler()));
tv1.setMovementMethod(LinkMovementMethod.getInstance());
}
public class GameTagHandler implements TagHandler {
private int startIndex = 0;
private int stopIndex = 0;
@Override
public void handleTag(boolean opening, String tag, Editable output, XMLReader xmlReader) {
if (tag.toLowerCase().equals("g")) {
if (opening) {
startGame(tag, output, xmlReader);
} else {
endGame(tag, output, xmlReader);
}
}
}
public void startGame(String tag, Editable output, XMLReader xmlReader) {
String cc;
try {
cc = (String) xmlReader.getProperty("color");
} catch (SAXNotRecognizedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SAXNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
startIndex = output.length();
}
public void endGame(String tag, Editable output, XMLReader xmlReader) {
stopIndex = output.length();
output.setSpan(new GameSpan(), startIndex, stopIndex, Spanned.SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE);
String cc;
try {
cc = (String) xmlReader.getProperty("color");
} catch (SAXNotRecognizedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SAXNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private class GameSpan extends ClickableSpan implements OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Log.e("asdf", "sdsdfs");
}
}
}
}
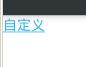
String s = "<g color='blue'>自定义</g>";
try {
SAXParserFactory factory = SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
SAXParser parser = factory.newSAXParser();
XMLReader reader = parser.getXMLReader();
MyContentHandler sss = new MyContentHandler();
reader.setContentHandler(sss);
reader.parse(new InputSource(new StringReader(s)));
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SAXException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}import org.xml.sax.Attributes;
import org.xml.sax.ContentHandler;
import org.xml.sax.Locator;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
public class MyContentHandler implements ContentHandler {
private StringBuffer buf;
public void setDocumentLocator( Locator locator ) {
}
public void startDocument() throws SAXException {
buf=new StringBuffer();
System.out.println("*******开始解析文档*******");
}
public void endDocument() throws SAXException {
System.out.println("*******解析文档结束*******");
}
public void processingInstruction( String target, String instruction )
throws SAXException {
}
public void startPrefixMapping( String prefix, String uri ) {
System.out.println("\n前缀映射: " + prefix +" 开始!"+ " 它的URI是:" + uri);
}
public void endPrefixMapping( String prefix ) {
System.out.println("\n前缀映射: "+prefix+" 结束!");
}
public void startElement( String namespaceURI, String localName,
String fullName, Attributes attributes )
throws SAXException {
System.out.println("\n 元素: " + "["+fullName+"]" +" 开始解析!");
// 打印出属性信息
for ( int i = 0; i < attributes.getLength(); i++ ) {
System.out.println("\t属性名称:" + attributes.getLocalName(i)
+ " 属性值:" + attributes.getValue(i));
}
}
public void endElement( String namespaceURI, String localName,
String fullName )
throws SAXException {
//打印出非空的元素内容并将StringBuffer清空
String nullStr="";
if (!buf.toString().trim().equals(nullStr)){
System.out.println("\t内容是: " + buf.toString().trim());
}
buf.setLength(0);
//打印元素解析结束信息
System.out.println("元素: "+"["+fullName+"]"+" 解析结束!");
}
public void characters( char[] chars, int start, int length )
throws SAXException {
//将元素内容累加到StringBuffer中
buf.append(chars,start,length);
}
public void ignorableWhitespace( char[] chars, int start, int length )
throws SAXException {
}
public void skippedEntity( String name ) throws SAXException {
}
}