SetPointer(HourGlass!)
ole_object=create oleobject
li = ole_object.ConnectToNewObject( "excel.application" )
if li<>0 then
messagebox('错误','请安装正确的excel版本!')
DESTROY ole_object
return
end if
ole_object.Workbooks.Open(ls_pathname)
ls_savename="c:\temp.txt"
IF FileExists(ls_savename) then FileDelete(ls_savename)
ole_object.activeworkbook.saveas(ls_savename,3)
ole_object.displayalerts=false
ole_object.quit()
ole_object.DisconnectObject()
DESTROY ole_object
//////////////////////////////////////////////////
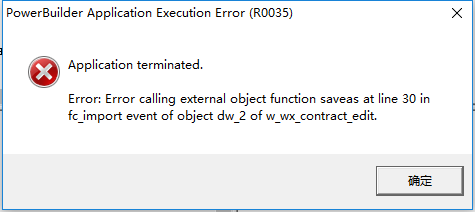
上面 saveas 部份电脑执行成功,部份电脑执行不成功。 报如下错,哪位pb达人遇到过,帮忙解决
 发帖
发帖 与我相关
与我相关 我的任务
我的任务 分享
分享