环境:Oracle 11.2.4.0 RAC
问题描述:
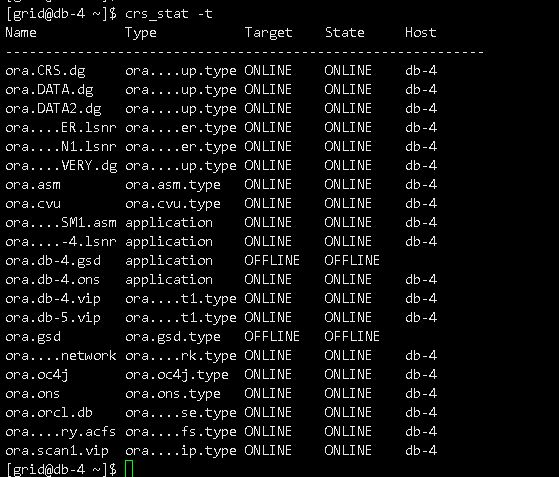
CRS服务不正常,asm diskgroup挂载不了,截图如下:
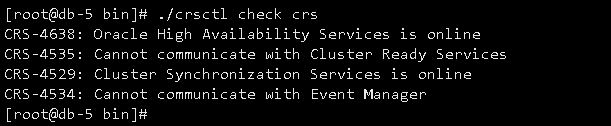

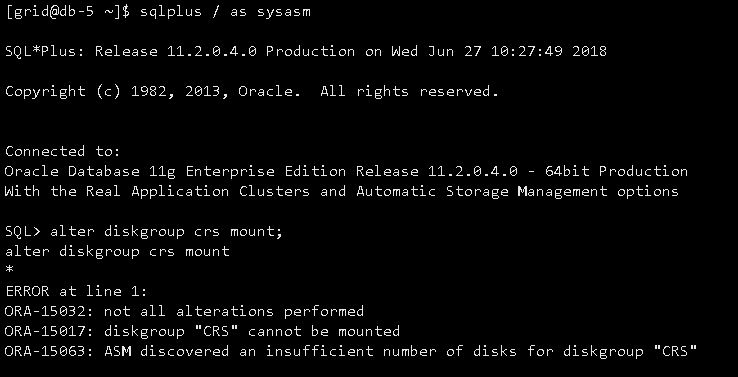
日志如下:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Wed Jun 27 10:28:10 2018
SQL> alter diskgroup crs mount
NOTE: cache registered group CRS number=1 incarn=0xdbd84eae
NOTE: cache began mount (not first) of group CRS number=1 incarn=0xdbd84eae
WARNING: detected duplicate paths to the same disk:
'/dev/mapper/CRSp1' and
'/dev/dm-23'
More trace information dumped to '/u01/app/grid/diag/asm/+asm/+ASM2/trace/+ASM2_ora_42445.trc'
Wed Jun 27 10:28:11 2018
ERROR: no read quorum in group: required 2, found 0 disks
NOTE: cache dismounting (clean) group 1/0xDBD84EAE (CRS)
NOTE: messaging CKPT to quiesce pins Unix process pid: 42445, image: oracle@db-5 (TNS V1-V3)
NOTE: dbwr not being msg'd to dismount
NOTE: lgwr not being msg'd to dismount
NOTE: cache dismounted group 1/0xDBD84EAE (CRS)
NOTE: cache ending mount (fail) of group CRS number=1 incarn=0xdbd84eae
NOTE: cache deleting context for group CRS 1/0xdbd84eae
GMON dismounting group 1 at 10 for pid 24, osid 42445
ERROR: diskgroup CRS was not mounted
WARNING: Disk Group CRS containing spfile for this instance is not mounted
WARNING: Disk Group CRS containing configured OCR is not mounted
WARNING: Disk Group CRS containing voting files is not mounted
ORA-15032: not all alterations performed
ORA-15017: diskgroup "CRS" cannot be mounted
ORA-15063: ASM discovered an insufficient number of disks for diskgroup "CRS"
ERROR: alter diskgroup crs mount
Wed Jun 27 10:28:13 2018
NOTE: No asm libraries found in the system
ERROR: -5(Duplicate disk DATA:DATA_0008)
ERROR: -5(Duplicate disk DATA:DATA_0001)
ERROR: -5(Duplicate disk DATA:DATA_0000)
ERROR: -5(Duplicate disk DATA:DATA_0003)
ERROR: -5(Duplicate disk CRS:CRS_0000)
ERROR: -5(Duplicate disk DATA:DATA_0007)
ERROR: -5(Duplicate disk DATA:DATA_0005)
ERROR: -5(Duplicate disk DATA2:DATA2_0002)
ERROR: -5(Duplicate disk DATA2:DATA2_0003)
ERROR: -5(Duplicate disk DATA:DATA_0004)
ERROR: -5(Duplicate disk RECOVERY:RECOVERY_0000)
ERROR: -5(Duplicate disk DATA:DATA_0002)
ERROR: -5(Duplicate disk DATA:DATA_0006)
ASM Health Checker found 1 new failures
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
分析:
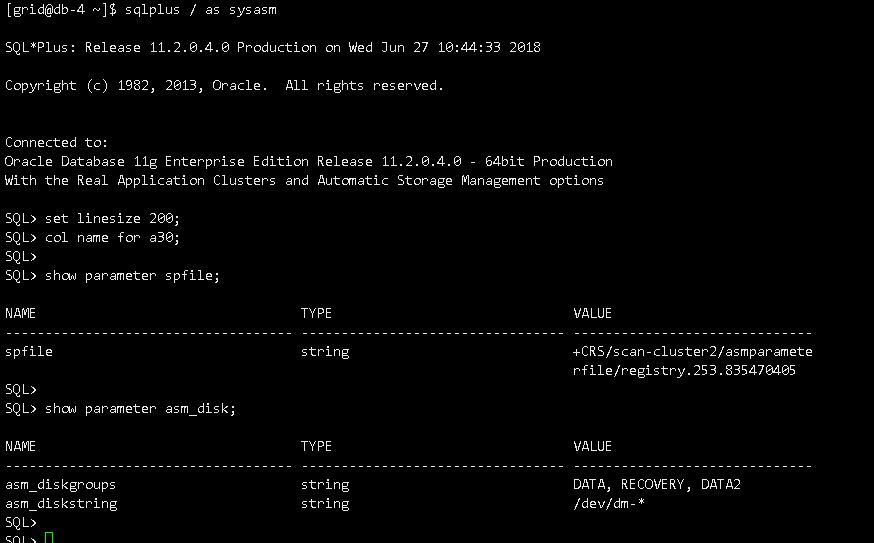
asm_diskstring里存在指向重复的路径:
/dev/*,/dev/mapper/*
造成日志中的提示:
----------------------------
WARNING: detected duplicate paths to the same disk:
'/dev/mapper/CRSp1' and
'/dev/dm-23'
--------------------------------------------------
修改asm_diskstring,无法修改:
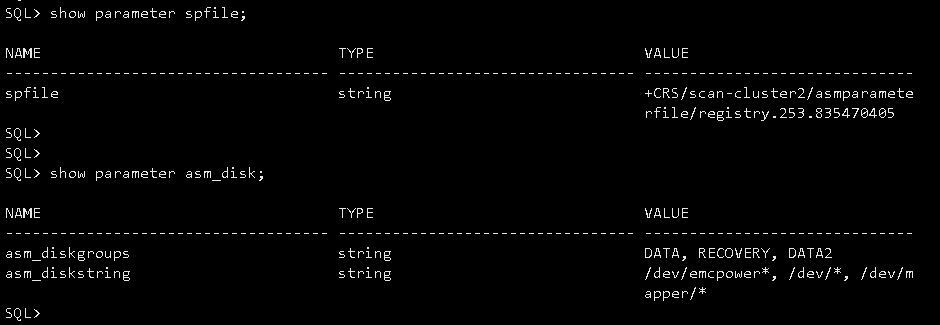
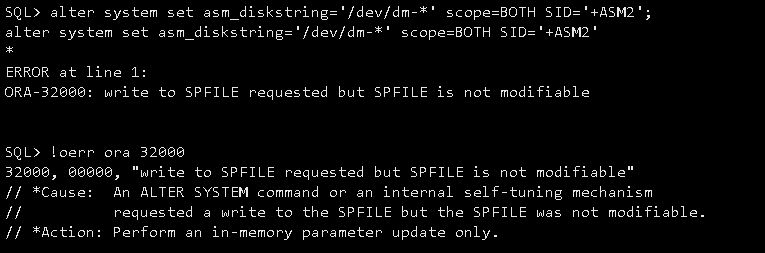
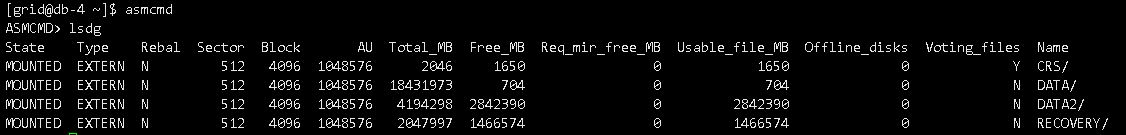
另一个节点正常,截图如下:
 发帖
发帖 与我相关
与我相关 我的任务
我的任务 分享
分享









