575
社区成员
 发帖
发帖 与我相关
与我相关 我的任务
我的任务 分享
分享以Python 3.9.7版本为主
Python 是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言
特点:易于学习、阅读、维护、跨平台、可扩展等
| 编号 | 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | abs(x) | 将x值转为绝对值 |
| 2 | ceil(x) | 将x值向上取整,比如:6.01,返回值7只要是大于本身,都会向上+1 |
| 3 | floor(x) | 将x值向下取整,比如:6.9,返回值6取本身值 |
| 4 | cmp(x,y) | Python3 已不再使用该函数,可用以下方式代替:(x>y)-(x<y) |
| 5 | exp(x) | 返回自然常数e的x次幂 |
| 6 | fabs(x) | 将x值转为浮点绝对值 |
| 7 | log(x) | 获取x值y为底数的次幂值,100=10^2 |
自然数e=2.718281828,所以在math.exp(1)=e^1=2.718281828
函数前记得加math前缀
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Feb 12, 2022 11:00 AM
import math
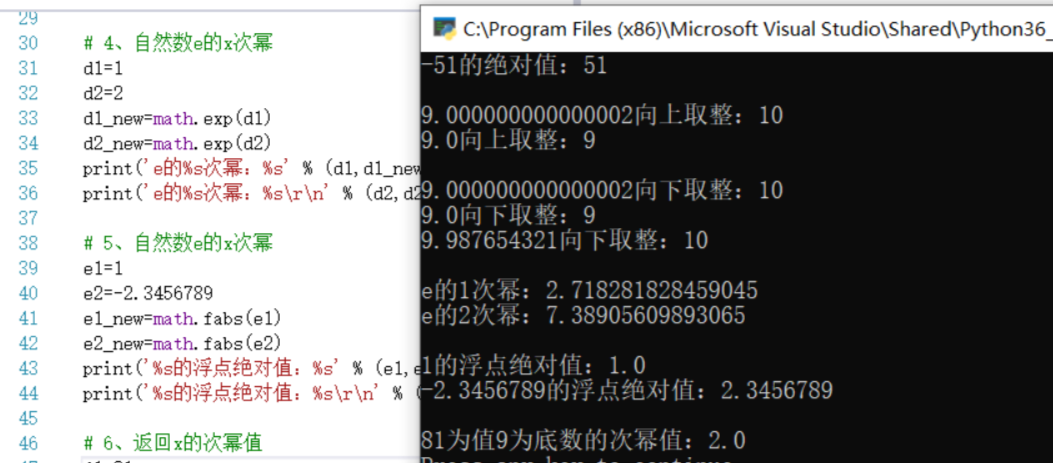
# 1、绝对值
a=-51
a_new=abs(a)
print('%s的绝对值:%s\r\n' % (a,a_new))
# 2、向上取整+1
b1=9.000000000000001
b2=9.0000000000000001
b1_new=math.ceil(b1)
b2_new=math.ceil(b2)
print('%s向上取整:%s' % (b1,b1_new))
print('%s向上取整:%s\r\n' % (b2,b2_new))
# 3、向下取整
c1=9.000000000000001
c2=9.0000000000000001
c3=9.987654321
c1_new=math.ceil(c1)
c2_new=math.ceil(c2)
c3_new=math.ceil(c3)
print('%s向下取整:%s' % (c1,c1_new))
print('%s向下取整:%s' % (c2,c2_new))
print('%s向下取整:%s\r\n' % (c3,c3_new))
# 4、自然数e的x次幂
d1=1
d2=2
d1_new=math.exp(d1)
d2_new=math.exp(d2)
print('e的%s次幂:%s' % (d1,d1_new))
print('e的%s次幂:%s\r\n' % (d2,d2_new))
# 5、自然数e的x次幂
e1=1
e2=-2.3456789
e1_new=math.fabs(e1)
e2_new=math.fabs(e2)
print('%s的浮点绝对值:%s' % (e1,e1_new))
print('%s的浮点绝对值:%s\r\n' % (e2,e2_new))
# 6、返回x的次幂值
f1=81
f2=9
f1_new=math.log(f1,f2)
print('%s为值%s为底数的次幂值:%s' % (f1,f2,f1_new))