176
社区成员
 发帖
发帖 与我相关
与我相关 我的任务
我的任务 分享
分享
| information | Detail |
| Class Link | https://bbs.csdn.net/forums/ssynkqtd-04 |
| Project requirement | https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/617332156 |
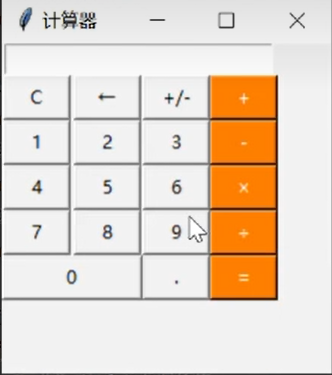
| The Aim of This Assignment | Develop a visual calculator |
| MU STU ID and FZU STU ID | 832101120/21126518 |
| Personal Software Process Stages | Estimated Time(minutes) | Actual Time(minutes) |
| Planning | 50 | 60 |
| • Estimate | 50 | 60 |
| Development | 300 | 350 |
| • Analysis | 20 | 20 |
| • Design Spec | 20 | 20 |
| • Design Review | 10 | 10 |
| • Coding Standard | 10 | 10 |
| • Design | 60 | 60 |
| • Coding | 100 | 150 |
| • Code Review | 50 | 50 |
| • Test | 30 | 30 |
| • Analysis | 100 | 120 |
| Reporting | 60 | 70 |
| • Test Repor | 10 | 10 |
| • Size Measurement | 30 | 40 |
| Sum | 450 | 530 |
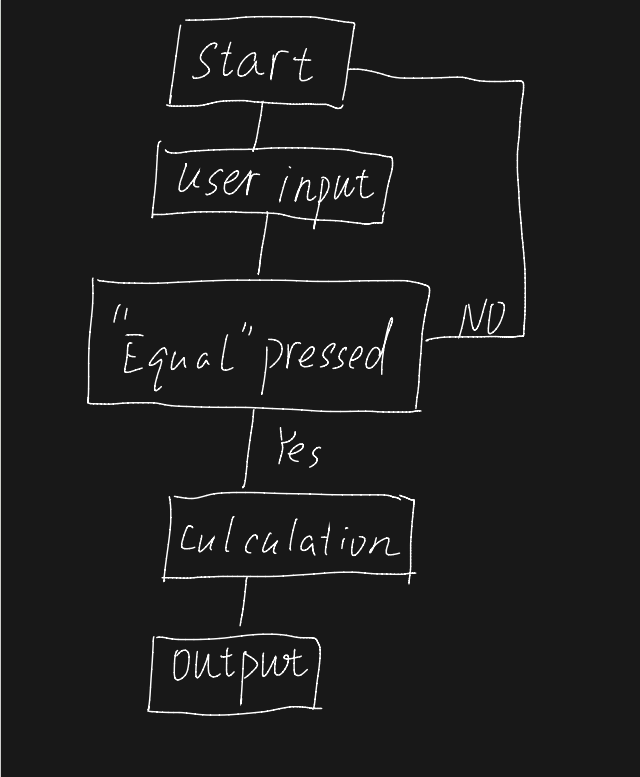
①How I think about the question
On this issue, the first thing I think about is how to achieve the function of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, and how to achieve the visual interface, how to design the visual interface, and finally I choose to use Python to achieve these functions.
②Find Information
After reading and learning related materials on CSDN, Github, and I learned the tkinter module can be used in this project.
③Design and Implementation process
First design the visual calculator interface, size, title and so on. Then design interactive buttons to achieve functions
import tkinter
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.minsize(280, 500)
result = tkinter.StringVar()
result.set(0)
result2 = tkinter.StringVar()
label = tkinter.Label(root, font=('宋体', 20), bg='#EEE9E9', bd='9', fg='#828282', anchor='se', textvariable
=result2)
label.place(width=280, height=170)
label2 = tkinter.Label(root, font=('宋体', 30), bg='#EEE9E9', bd='9', fg='black', anchor='se', textvariable
=result)
label2.place(y=170, width=280, height=60)
# Numbers buttons
btn7 = tkinter.Button(root, text='7', font=('宋体', 20), fg=('#4F4F4F'), bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressNum('7'))
btn7.place(x=0, y=285, width=70, height=55)
btn8 = tkinter.Button(root, text='8', font=('宋体', 20), fg=('#4F4F4F'), bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressNum('8'))
btn8.place(x=70, y=285, width=70, height=55)
btn9 = tkinter.Button(root, text='9', font=('宋体', 20), fg=('#4F4F4F'), bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressNum('9'))
btn9.place(x=140, y=285, width=70, height=55)
btn4 = tkinter.Button(root, text='4', font=('宋体', 20), fg=('#4F4F4F'), bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressNum('4'))
btn4.place(x=0, y=340, width=70, height=55)
btn5 = tkinter.Button(root, text='5', font=('宋体', 20), fg=('#4F4F4F'), bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressNum('5'))
btn5.place(x=70, y=340, width=70, height=55)
btn6 = tkinter.Button(root, text='6', font=('宋体', 20), fg=('#4F4F4F'), bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressNum('6'))
btn6.place(x=140, y=340, width=70, height=55)
btn1 = tkinter.Button(root, text='1', font=('宋体', 20), fg=('#4F4F4F'), bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressNum('1'))
btn1.place(x=0, y=395, width=70, height=55)
btn2 = tkinter.Button(root, text='2', font=('宋体', 20), fg=('#4F4F4F'), bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressNum('2'))
btn2.place(x=70, y=395, width=70, height=55)
btn3 = tkinter.Button(root, text='3', font=('宋体', 20), fg=('#4F4F4F'), bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressNum('3'))
btn3.place(x=140, y=395, width=70, height=55)
btn0 = tkinter.Button(root, text='0', font=('宋体', 20), fg=('#4F4F4F'), bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressNum('0'))
btn0.place(x=70, y=450, width=70, height=55)
# Operation symbol buttons
btnac = tkinter.Button(root, text='AC', bd=0.5, font=('黑体', 20), fg='orange', command=lambda: pressCompute('AC'))
btnac.place(x=0, y=230, width=70, height=55)
btnback = tkinter.Button(root, text='←', font=('宋体', 20), fg='#4F4F4F', bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressCompute('b'))
btnback.place(x=70, y=230, width=70, height=55)
btndivi = tkinter.Button(root, text='÷', font=('宋体', 20), fg='#4F4F4F', bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressCompute('/'))
btndivi.place(x=140, y=230, width=70, height=55)
btnmul = tkinter.Button(root, text='×', font=('宋体', 20), fg="#4F4F4F", bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressCompute('*'))
btnmul.place(x=210, y=230, width=70, height=55)
btnsub = tkinter.Button(root, text='-', font=('宋体', 20), fg=('#4F4F4F'), bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressCompute('-'))
btnsub.place(x=210, y=285, width=70, height=55)
btnadd = tkinter.Button(root, text='+', font=('宋体', 20), fg=('#4F4F4F'), bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressCompute('+'))
btnadd.place(x=210, y=340, width=70, height=55)
btnequ = tkinter.Button(root, text='=', bg='orange', font=('宋体', 20), fg=('#4F4F4F'), bd=0.5, command=
lambda: pressEqual())
btnequ.place(x=210, y=395, width=70, height=110)
btnper = tkinter.Button(root, text='%', font=('宋体', 20), fg=('#4F4F4F'), bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressCompute('%'))
btnper.place(x=0, y=450, width=70, height=55)
btnpoint = tkinter.Button(root, text='.', font=('宋体', 20), fg=('#4F4F4F'), bd=0.5, command=lambda:
pressCompute('.'))
btnpoint.place(x=140, y=450, width=70, height=55)
# Operating function
lists = []
isPressSign = False
isPressNum = False
# Numerical function
def pressNum(num):
global lists
global isPressSign
if isPressSign == False:
pass
else:
result.set(0)
isPressSign = False
oldnum = result.get()
if oldnum == '0':
result.set(num)
else:
newnum = oldnum + num
result.set(newnum)
# Operational function
def pressCompute(sign):
global lists
global isPressSign
num = result.get()
lists.append(num)
lists.append(sign)
isPressSign = True
if sign == 'AC':
lists.clear()
result.set(0)
if sign == 'b':
a = num[0:-1]
lists.clear()
result.set(a)
# Gets the result function
def pressEqual():
global lists
global isPressSign
curnum = result.get()
lists.append(curnum)
computrStr = ''.join(lists)
endNum = eval(computrStr)
# a = str(endNum)
# b = '='+a
# c = b[0:10]
result.set(endNum)
result2.set(computrStr)
lists.clear()
root.mainloop()
In this project, I implemented some features I didn't know about before, such as python's tkinter library. I spend a lot of time searching the Internet for relevant information (this part of the time I calculate into code). If I want to use python to develop some small programs similar to calculators in the future, I should have a further understanding of the function library such as tkinter, which has great practical significance, enhance the search ability and reduce the time for searching unknown knowledge.