70,040
社区成员
 发帖
发帖 与我相关
与我相关 我的任务
我的任务 分享
分享#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#define infile "infile.dat"
#define outfile "outfile.dat"
sem_t f1;
sem_t f2;
void inputdata()
{
int infd;
char buf[50];
if ((infd = open(infile, O_WRONLY | O_TRUNC | O_CREAT, 10700)) == -1)
{
printf("ERROR, OPEN READ FILE FAILED:%s \n", sys_errlist[errno]);
exit(255);
}
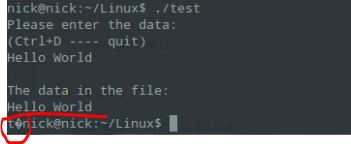
printf("Please enter the data:\n");
printf("(Ctrl+D ---- quit)\n");
while(fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin))
{
if (write(infd, buf, strlen(buf)) != strlen(buf))
{
printf("ERROR, WRITE FILE FAILED:%s \n", sys_errlist[errno]);
exit(255);
}
}
close(infd);
sem_post(&f1);
}
void copydata()
{
sem_wait(&f1);
int infd, outfd;
char buf[50];
if ((infd = open(infile, O_RDONLY))==-1)
{
printf("ERROR, OPEN READ FILE FAILED:%s \n", sys_errlist[errno]);
exit(255);
}
if ((outfd = open(outfile, O_WRONLY | O_TRUNC | O_CREAT, 10700))==-1)
{
printf("ERROR, OPEN WRITE FILE FAILED:%s \n", sys_errlist[errno]);
exit(255);
}
int count;
while((count = read(infd, buf, sizeof(buf))) > 0)
{
if (count != write(outfd, buf, count))
{
printf("ERROR, WRITE FILE FAILED:%s \n", sys_errlist[errno]);
exit(255);
}
}
close(infd);
close(outfd);
sem_post(&f2);
}
void showdata()
{
sem_wait(&f2);
int outfd;
char buf[50];
if ((outfd = open(outfile, O_RDONLY, 10700))==-1)
{
printf("ERROR, OPEN WRITE FILE FAILED:%s \n", sys_errlist[errno]);
exit(255);
}
int count;
printf("\nThe data in the file:\n");
while((count = read(outfd, buf, sizeof(buf))) > 0)
{
printf("%s", buf);
}
close(outfd);
}
void main()
{
pthread_t t1,t2,t3,t4;
sem_init(&f1,0,0);
sem_init(&f2,0,0);
pthread_create(&t1,NULL, (void *)showdata, NULL);
pthread_create(&t2,NULL, (void *)copydata, NULL);
pthread_create(&t3,NULL, (void *)inputdata, NULL);
pthread_join(t1,NULL);
}
void HexDump(char *buf,int len,int addr) {
int i,j,k;
char binstr[80];
for (i=0;i<len;i++) {
if (0==(i%16)) {
sprintf(binstr,"%08x -",i+addr);
sprintf(binstr,"%s %02x",binstr,(unsigned char)buf[i]);
} else if (15==(i%16)) {
sprintf(binstr,"%s %02x",binstr,(unsigned char)buf[i]);
sprintf(binstr,"%s ",binstr);
for (j=i-15;j<=i;j++) {
sprintf(binstr,"%s%c",binstr,('!'<buf[j]&&buf[j]<='~')?buf[j]:'.');
}
printf("%s\n",binstr);
} else {
sprintf(binstr,"%s %02x",binstr,(unsigned char)buf[i]);
}
}
if (0!=(i%16)) {
k=16-(i%16);
for (j=0;j<k;j++) {
sprintf(binstr,"%s ",binstr);
}
sprintf(binstr,"%s ",binstr);
k=16-k;
for (j=i-k;j<i;j++) {
sprintf(binstr,"%s%c",binstr,('!'<buf[j]&&buf[j]<='~')?buf[j]:'.');
}
printf("%s\n",binstr);
}
}
//iconv_linux下字符集编码转换轻松实现
(1) iconv_t iconv_open(const char *tocode, const char *fromcode);
//此函数说明将要进行哪两种编码的转换,tocode是目标编码,fromcode是原编码,该函数返回一个转换句柄,供以下两个函数使用。
(2) size_t iconv(iconv_t cd,char **inbuf,size_t *inbytesleft,char **outbuf,size_t *outbytesleft);
//此函数从inbuf中读取字符,转换后输出到outbuf中,inbytesleft用以记录还未转换的字符数,outbytesleft用以记录输出缓冲的剩余空间。
(3) int iconv_close(iconv_t cd);
//此函数用于关闭转换句柄,释放资源。
//例子1: 用C语言实现的转换示例程序
/* f.c : 代码转换示例C程序 */
#include <iconv.h>
#define OUTLEN 255
main()
{
char *in_utf8 = "姝e?ㄥ??瑁?";
char *in_gb2312 = "正在安装";
char out[OUTLEN];
/*unicode码转为gb2312码*/
rc = u2g(in_utf8,strlen(in_utf8),out,OUTLEN);
printf("unicode-->gb2312 out=%sn",out);
//gb2312码转为unicode码
rc = g2u(in_gb2312,strlen(in_gb2312),out,OUTLEN);
printf("gb2312-->unicode out=%sn",out);
}
/*代码转换:从一种编码转为另一种编码*/
int code_convert(char *from_charset,char *to_charset,char *inbuf,int inlen,char *outbuf,int outlen)
{
iconv_t cd;
int rc;
char **pin = &inbuf;
char **pout = &outbuf;
cd = iconv_open(to_charset,from_charset);
if (cd==0) return -1;
memset(outbuf,0,outlen);
if (iconv(cd,pin,&inlen,pout,&outlen)==-1) return -1;
iconv_close(cd);
return 0;
}
/*UNICODE码转为GB2312码*/
int u2g(char *inbuf,int inlen,char *outbuf,int outlen)
{
return code_convert("utf-8","gb2312",inbuf,inlen,outbuf,outlen);
}
/*GB2312码转为UNICODE码*/
int g2u(char *inbuf,size_t inlen,char *outbuf,size_t outlen)
{
return code_convert("gb2312","utf-8",inbuf,inlen,outbuf,outlen);
}
//例子2: 用C++语言实现的转换示例程序
/* f.cpp : 代码转换示例C++程序 */
#include <iconv.h>
#include <iostream>
#define OUTLEN 255
using namespace std;
// 代码转换操作类
class CodeConverter {
private:
iconv_t cd;
public:
// 构造
CodeConverter(const char *from_charset,const char *to_charset) {
cd = iconv_open(to_charset,from_charset);
}
// 析构
~CodeConverter() {
iconv_close(cd);
}
// 转换输出
int convert(char *inbuf,int inlen,char *outbuf,int outlen) {
char **pin = &inbuf;
char **pout = &outbuf;
memset(outbuf,0,outlen);
return iconv(cd,pin,(size_t *)&inlen,pout,(size_t *)&outlen);
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char *in_utf8 = "姝e?ㄥ??瑁?";
char *in_gb2312 = "正在安装";
char out[OUTLEN];
// utf-8-->gb2312
CodeConverter cc = CodeConverter("utf-8","gb2312");
cc.convert(in_utf8,strlen(in_utf8),out,OUTLEN);
cout << "utf-8-->gb2312 in=" << in_utf8 << ",out=" << out << endl;
// gb2312-->utf-8
CodeConverter cc2 = CodeConverter("gb2312","utf-8");
cc2.convert(in_gb2312,strlen(in_gb2312),out,OUTLEN);
cout << "gb2312-->utf-8 in=" << in_gb2312 << ",out=" << out << endl;
}
二、利用iconv命令进行编码转换
iconv命令用于转换指定文件的编码,默认输出到标准输出设备,亦可指定输出文件。
用法: iconv [选项...] [文件...]
有如下选项可用:
输入/输出格式规范:
-f, --from-code=名称 原始文本编码
-t, --to-code=名称 输出编码
信息:
-l, --list 列举所有已知的字符集
输出控制:
-c 从输出中忽略无效的字符
-o, --output=FILE 输出文件
-s, --silent 关闭警告
--verbose 打印进度信息
-?, --help 给出该系统求助列表
--usage 给出简要的用法信息
-V, --version 打印程序版本号
例子:
iconv -f utf-8 -t gb2312 aaa.txt >bbb.txt
这个命令读取aaa.txt文件,从utf-8编码转换为gb2312编码,其输出定向到bbb.txt文件。
小结: Linux为我们提供了强大的编码转换工具,给我们带来了方便。
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#define infile "infile.dat"
#define outfile "outfile.dat"
sem_t f1;
sem_t f2;
void inputdata()
{
int infd;
char buf[50];
if ((infd = open(infile, O_WRONLY | O_TRUNC | O_CREAT, 10700)) == -1)
{
printf("ERROR, OPEN READ FILE FAILED:%s \n", sys_errlist[errno]);
//printf("ERROR, OPEN READ FILE FAILED:%s \n", strerror(errno));
exit(255);
}
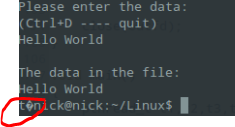
printf("Please enter the data:\n");
printf("(Ctrl+D ---- quit)\n");
while(fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin))
{
if (write(infd, buf, strlen(buf)) != strlen(buf)) {
printf("ERROR, WRITE FILE FAILED:%s \n", sys_errlist[errno]);
//printf("ERROR, WRITE FILE FAILED:%s \n", strerror(errno));
exit(255);
}
}
close(infd);
sem_post(&f1);
}
void copydata()
{
sem_wait(&f1);
int infd, outfd;
char buf[50];
if ((infd = open(infile, O_RDONLY))==-1)
{
printf("ERROR, OPEN READ FILE FAILED:%s \n", sys_errlist[errno]);
//printf("ERROR, OPEN READ FILE FAILED:%s \n", strerror(errno));
exit(255);
}
if ((outfd = open(outfile, O_WRONLY | O_TRUNC | O_CREAT, 10700))==-1)
{
printf("ERROR, OPEN WRITE FILE FAILED:%s \n", sys_errlist[errno]);
//printf("ERROR, OPEN WRITE FILE FAILED:%s \n", strerror(errno));
exit(255);
}
int count;
while((count = read(infd, buf, sizeof(buf))) > 0)
{
if (count != write(outfd, buf, count))
{
printf("ERROR, WRITE FILE FAILED:%s \n", sys_errlist[errno]);
//printf("ERROR, WRITE FILE FAILED:%s \n", strerror(errno));
exit(255);
}
}
close(infd);
close(outfd);
sem_post(&f2);
}
void showdata()
{
sem_wait(&f2);
int outfd;
char buf[50];
if ((outfd = open(outfile, O_RDONLY, 10700))==-1)
{
printf("ERROR, OPEN WRITE FILE FAILED:%s \n", sys_errlist[errno]);
//printf("ERROR, OPEN WRITE FILE FAILED:%s \n", strerror(errno));
exit(255);
}
int count;
printf("\nThe data in the file:\n");
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); /*初始化缓存为0*/
while((count = read(outfd, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1)) > 0) /*防止读到的数据是50个字符,最后一个字符用于字符串结束标记 '\0' */
{
printf("count = %d\n", count);
printf("%s", buf);
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); /*初始化缓存为0*/
}
close(outfd);
}
int main(void)
{
pthread_t t1,t2,t3,t4;
sem_init(&f1,0,0);
sem_init(&f2,0,0);
pthread_create(&t1,NULL, (void *)showdata, NULL);
pthread_create(&t2,NULL, (void *)copydata, NULL);
pthread_create(&t3,NULL, (void *)inputdata, NULL);
pthread_join(t1,NULL);
return 0;
}